LiFePO4 Battery Packs: How It Works and What It's For
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) battery packs are becoming increasingly popular due to their safety, durability and efficiency. In this article, we will look at how these batteries work, what components are used, and what they can be useful for.
What are LiFePO4 Battery Packs?
LiFePO4 battery assemblies use lithium-iron-phosphate batteries, which are characterized by high stability and a long service life. The main advantages of these batteries include:
- Durability: Usually have more than 2000 charge-discharge cycles.
- Safety: They have high thermal and chemical stability, which reduces the risk of overheating and explosion.
- Environmentally friendly: Contains less toxic materials compared to other types of lithium batteries.
How Does a LiFePO4 Battery Pack Work?
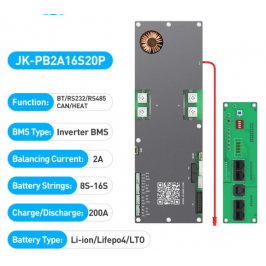
A LiFePO4 battery pack consists of several individual battery cells assembled together to achieve the required capacity and voltage. The main elements of the assembly:
-
Battery Cells: The main component that stores and supplies electrical energy.
-
BMS (Battery Management System): A battery management system that monitors the condition of batteries, ensures their safety and extends their service life. BMS performs the following functions:
- Overcharge and overdischarge protection: Prevents batteries from leaving the safe voltage range.
- Balance: Ensures that all elements of the battery pack are charged and discharged evenly.
- Temperature monitoring: Protects batteries from overheating.
-
Connection: Battery cells are connected by wires or buses to achieve the required voltage and capacity configuration.
Configurations 4s, 8s and 16s: How Does It Work?
In LiFePO4 systems, the terms 4s, 8s and 16s describe specific battery cell connection configurations:
-
4s (4-Series): This is an assembly of 4 battery cells connected in series. Each cell has a standard voltage, for example 3.2 V. When connected in series, the voltage increases, resulting in a battery with a voltage of 12.8 V (4 x 3.2 V). The 4s configuration provides higher voltage while maintaining the capacity of each cell, making it ideal for many domestic and industrial applications.
-
8s (8-Series): This configuration includes 8 battery cells connected in series. This provides a higher voltage, for example 25.6 V (8 x 3.2 V). The 8s configuration is typically used in systems requiring higher voltages, such as large electric vehicles or renewable energy systems.
-
16s (16-Series): An assembly of 16 battery cells provides an even higher voltage, for example 51.2 V (16 x 3.2 V). This could be used in powerful electric vehicles, large-scale energy storage systems or industrial applications. High voltage provides the possibility of powering powerful devices and systems.
How to Charge LiFePO4 Battery Assemblies?
Charging LiFePO4 battery assemblies requires a special charger that meets the characteristics of LiFePO4 batteries:
-
Charger: Use a charger that is designed for LiFePO4 batteries. It should be able to adjust the voltage and current according to the parameters of your battery pack. Make sure the charger has overcharge and overdischarge protection features.
-
BMS (Battery Management System): BMS helps control the charging process, preventing overcharging of batteries and ensuring their safety. It also provides cell balancing during charging.
-
Charging Process: When charging battery packs, it is important to follow the recommended voltage and current values to avoid damage to the cells.
How to assemble a LiFePO4 battery assembly yourself?
Assembling a LiFePO4 battery system yourself can be a difficult process, but if you follow the right instructions, it is possible:
-
Component Selection: You will need LiFePO4 battery cells, BMS, connecting wires or busbars, and a case for assembly.
-
Cell Connection: Place the battery cells in the desired configuration (4s, 8s, 16s). Connect the elements in series using the appropriate wires or busbars. Make sure all connections are secure and strong.
-
BMS Installation: Connect the Battery Management System (BMS) to the battery areas The BMS must be properly connected to each element to ensure accurate monitoring and protection.
-
Inspection and Testing: Before first use, check all connections and functionality of the system. Make sure all components are working properly and are free of defects.
New Offers: Batteries 280Ah
We are pleased to announce that new battery assemblies with a capacity of 280Ah will soon appear in our range. These powerful batteries will provide even more energy for your needs and will be ideal for applications in various fields, from electric vehicles to renewable energy systems.
What are LiFePO4 Battery Assemblies for?
LiFePO4 battery assemblies are used in various fields due to their advantages:
- Electric Vehicles: Electric scooters, bicycles and cars need reliable and durable batteries.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Used in solar and wind energy storage systems.
- Energy Backup Systems: To ensure uninterrupted power supply in the event of a power outage.
- Portable Devices: For powering various portable electronic devices and tools.
Conclusion
LiFePO4 battery packs are a great choice for those looking for reliability, durability and safety. Due to their efficient energy management, high stability and environmental friendliness, they are used in various fields, from electric transport to renewable energy systems. The new range of 280Ah batteries and different configurations such as 4s, 8s and 16s expand the possibilities of using these powerful batteries in different scenarios.
Proper charging and self-assembly of battery packs are also important to ensure their efficiency and longevity. By following the instructions and using the appropriate components, you will be able to create a reliable and productive battery system for your needs.